How to make confined space entry procedure
How to make confined space entry procedure
1.0 PURPOSE
This plan contains requirements for practices and procedures to protect employees from hazards associated with entry into permit-required confined spaces. This procedure shall be read in conjunction with your country enforcement body rules and regulations or as per ministerial orders
2.0 DEFINITIONS
a. Acceptable entry conditions. The conditions that must exist in a permit-required confined space to allow safe entry by personnel.
b. Attendant. The individual stationed outside a permitted space that monitors the Authorised Entrants and performs duties assigned.
c. Authorized Entrant. A person who is authorized to enter a permit space.
d. Confined space. A space that meets the following requirements:
(1) Is large enough and so that a worker can bodily enter & perform the assigned task; and
(2) Has limited or restricted means of entry & exit; and
(3) It is unsuitable for continuous human occupancy.
(4) Any tank, vat, pipe, furnace flue, sewer, manhole or similar area in which toxic, poisonous or otherwise dangerous fumes, dust or substances are liable to be present to such an extent as to involve a risk of a worker being overcome. Such fumes may be generated by the work being carried out.
(5) This definition shall include areas of oxygen deficiency or areas where the work is undertaken may produce a lack of oxygen.
e. Entry. The action by which a worker passes through an opening into a permit-required confined space. Entry is assumed to be as soon as the employee’s body breaks the plane of the opening.
f. Entry permit. The written document that is provided to allow and control entry into a permit-required confined space.
g. Entry Supervisor (Competent Person). The person is responsible for determining acceptable conditions prior to entry into a permit-required confined space and for terminating entry. Generally, the Safety Officer shall be the appointed Entry Supervisor.
h. Designated Official. The person is responsible for evaluating the potential for permit-required confined spaces and ensuring program elements are enforced. Generally, the Safety Officer shall be the Designated Official.
i. Hazardous atmosphere. An atmosphere that may expose employees to risk of death or injury from one or more of the following causes:
(1) Flammable gases or vapors in excess of 10 percent of the lower flammable limit limit
Lower flammable limit (LFL).
(2) Airborne combustible dust in a concentration equal to or greater than its LFL.
(3) Atmospheric oxygen less than 19.5% or greater than 23.5%.
(4) The atmospheric concentration of any substance that has a permissible exposure limit (PEL).
(5) Any other atmospheric condition that is immediately dangerous to life and health (IDLH); toxic, poisonous or otherwise dangerous fumes.
j. Permit-required confined space. A confined space that has one or more of the below-mentioned characteristics;
(1) confined space can contain or has the potential of containing a hazardous atmosphere.
(2) It contains a material that has the potential to engulf an entrant.
(3) Has an internal configuration in which an entrant could be asphyxiated or trapped by slopes or inwardly converging walls or downward & tapers to a small cross-section.
(4) Contains any other different recognized serious safety and health hazard.
k. Permit System. The written procedures for preparing and issuing permits for entry and for returning the permit space to service upon the termination of entry.
l. Rescue team or service. The team designated to perform a rescue operation in permit-required spaces.
m. Retrieval system. The equipment used for non-entry rescue from permit-required spaces.
n. Testing. The process by which hazards are identified and evaluated for entry into permit-required spaces.
3.0 PROCEDURE
3.1 GENERAL
This procedure shall be read in conjunction with the Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs: or other enforcement bodies rules regulations being used in your country for Work in Confined Spaces.
The Project/ Safety Manager, Safety Officer, or other supervisory personnel shall evaluate, or designate a competent person to evaluate, the potential for permit-required confined spaces.
a. The evaluation shall use the definitions presented above to determine the presence of confined spaces. Reference shall be made to the Activity Hazard Analysis (AHA) or Risk Assessment for confined space entry evaluation.
b. All permit-required confined spaces shall be identified with a sign reading “A CONFINED SPACE – DO NOT ENTER – PERMIT REQUIRED” to inform personnel of the existence and location of, and the danger posed by, the permit-required confined space.
c. Entry into any confined space shall not be permitted until the permit system has been properly executed. The permit shall be conspicuously posted at the confined space. All Entrants shall be required to sign a log upon entering and exiting the confined space.
Employees shall undergo awareness training regarding the hazards of confined spaces and the procedures to be followed. Special training shall be provided to all Entry Supervisors, Authorised Entrants, and Attendants.
3.2 RESPONSIBILITIES
a. Authorized Entrants shall:
(1) Ensure that the log is signed upon entering and exiting the confined space.
(2) Communicate verbally with the Attendant as necessary so the Attendant can monitor Entrant status and alert Entrants of any need to evacuate the permit-required confined space. It is recommended that if VHF radio communication can be established between the Attendant and Entrants, it should be used.
(3) Evacuate the permit-required confined space and alert the Attendant whenever they recognize any warning signs or symptoms of exposure to a dangerous situation; they detect a prohibited condition; whenever the Attendant or Entry Supervisor orders evacuation; or when an evacuation alarm is activated by the oxygen meter.
b. Attendants shall:
- Be easily identified, properly trained and aware of the duties associated with each emergency situation that may occur within the confined space.
- Remain outside the permit-required confined space during entry operations until relieved by another attendant.
(3) Take action when conditions warrant evacuation of the permit-required confined space. Inform the Entry Supervisor of conditions, and persons approaching the permit-required confined space.
(4) Maintain an accurate list/log of personnel within the permit-required confined space and a means to identify the personnel.
(5) Communicate with Entrants as necessary to monitor them and to inform them of the need to evacuate.
(6) Immediately order the evacuation of the permit-required confined space if conditions change to pose a hazardous condition.
(7) Perform non-entry rescue as specified in the permit and summon rescue or other emergency services as necessary.
- Not perform any other duty other than that of the Attendant during permit-required confined space entry.
c. Entry Supervisor shall:
(1) must be competent and be capable of recognizing & evaluating worker’s exposure to unsafe conditions & hazardous substances, and is capable of specifying the necessary protection and precautions to be taken to ensure the safety of employees. Note: All confined spaces shall be evaluated for possible heat stress.
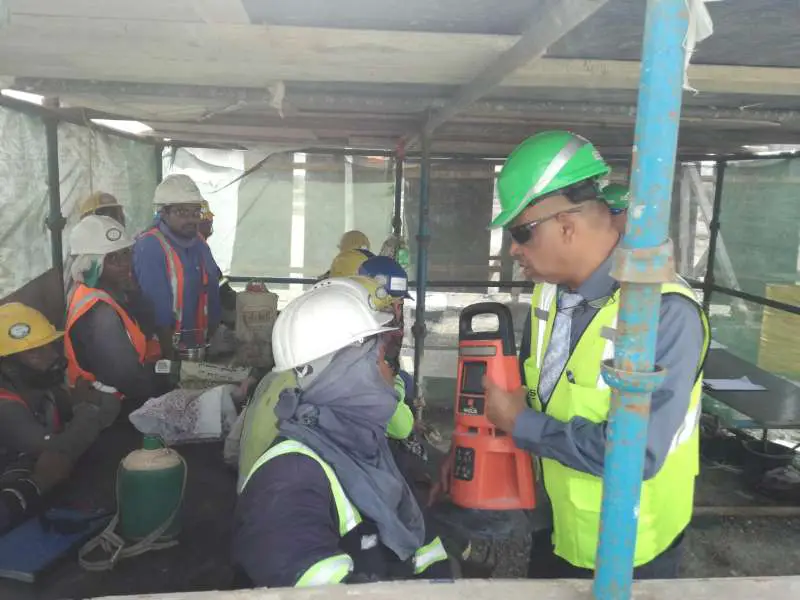

(2) Test the environment of the Confined Space with properly calibrated and approved equipment to identify a potentially hazardous atmosphere (i.e., oxygen-deficient or oxygen-enriched atmosphere, or an explosive atmosphere.
(3) Prohibit entry into a Confined Space if a hazardous atmosphere is found to exist or suspected of existing.
(4) Prepare and post the Confined Space Entry Permit.
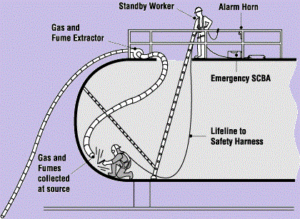
(5) Verify that all necessary equipment and procedures are in place prior to entry. All personnel entering a Confined Space shall wear a safety harness and lifeline. Ensure that one of the Entrants is wearing the oxygen/explosive meter on their person to monitor any changes in atmospheric conditions if practicable. How to make confined space entry procedure
(6) Instruct employees on the nature of the hazards involved, the necessary precautions to be taken, and the use of required protective equipment, especially respiratory protection.
(7) Terminate the entry when assigned work is completed or when conditions warrant evacuation.
(8) Verify that rescue services are available and that a means of summoning them is available.
(9) Ensure that entry operations are consistent with the terms of the entry permit and that acceptable conditions are maintained i.e.
Proper ventilation equipment is used to purge or supply air to the confined space,
All electrical service is low voltage or GFCI protected,
Adequate access/ egress from the confined space is provided,
A task-specific rescue plan has been developed and reviewed with all involved employees, and
All external sources of contamination are isolated.
3.3 TESTING & MONITORING
a. A Neotronics Mini-Gas Confined Space Monitor, or similar approved monitor, shall be available for testing purposes. The unit shall measure oxygen 0 – 25%, and combustible gas 0 – 100% LEL.
- The Safety Department shall be responsible for servicing the Neotronics monitors, including the installation and calibration of new oxygen and gas sensors. The units shall be serviced annually and calibration records maintained.
- All employees conducting air monitoring shall have proper documented training.
3.4 AIR SAMPLING PROTOCOL
As a minimum, monitoring for oxygen and explosive gasses shall be conducted in newly constructed confined spaces where little hazard of airborne contamination exists.
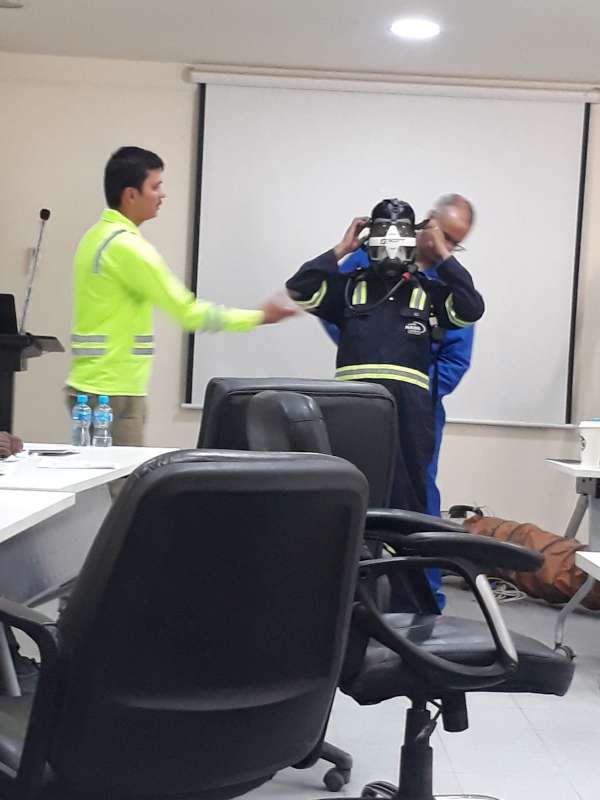

a. Samples of the ambient air in the confined space should be taken at different elevations inside the space by the Entry Supervisor, and the results recorded on the confined space permit.
b. After the Entry Supervisor completes the air sampling, the monitor is to be attached to the belt of the Entrant before he enters the confined space. This will provide the Entrant with a continuous readout and signal the Entrant of any changes in the atmospheric. (e.g. the level of oxygen in the air goes below 19.5%). How to make confined space entry procedure
3.5 PERMIT-REQUIRED CONFINED SPACE ENTRY PROCEDURES
Note: Permit to Work- Confined Space Entry shall be obtained from the Ministry of Works prior to enter any confined spaces; as well the procedures of COMPANY are applicable.
a. The Entry Supervisor shall implement a system for the preparation, issuance, and cancellation of confined space entry permits.
(1) Before entry commences, the Entry Supervisor identified on the permit shall sign the permit to authorize entry.
(2) The completed permit shall be posted at the entry portal so that Entrants can confirm that pre-entry preparations have been completed.
(3) The duration of the permit shall not exceed the time required to complete the task identified on the permit.
b. Plans and procedures shall be developed for the summoning of rescue personnel and for preventing unauthorized personnel from attempting a rescue.
c. The Entry Supervisor shall designate at least one attendant who will remain outside the permit-required confined space for the duration of the activity.
d. The Entry Supervisor shall ensure that, when more than one crew is authorized entry, the activities of one crew do not interfere with the work of another crew.
e. The Site Safety Manager shall review the entry program periodically to ensure that the measures contained in the program are still adequate.
3.6 TRAINING
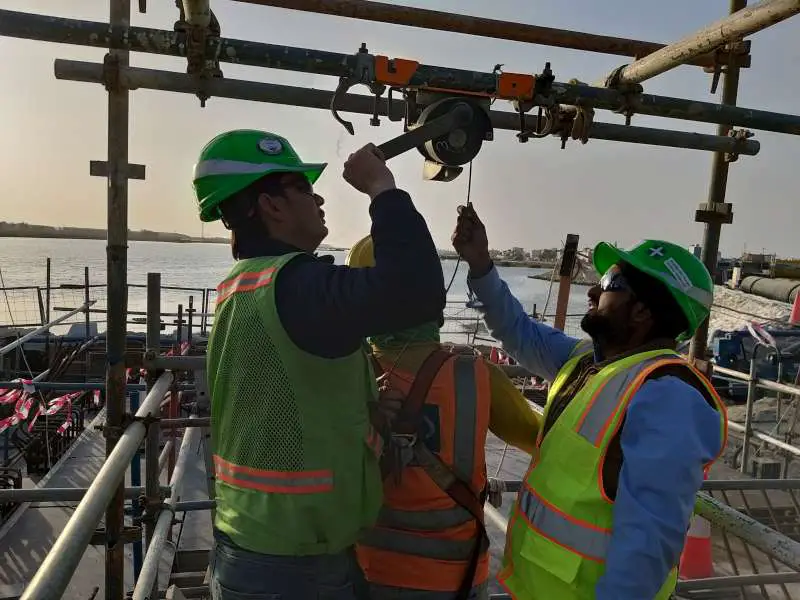

a. All employees shall be instructed not to enter permit-required confined spaces without the proper permit outlining procedures and practices for entering the space.
b. Employees who are required to enter permit-required confined spaces or act as Attendants or Entry Supervisors shall be trained in order to acquire the knowledge and skills necessary for the safe performance of their work. The employees must also be familiar with the types of hazards associated with the entry and the control measures used to ensure safe conditions.
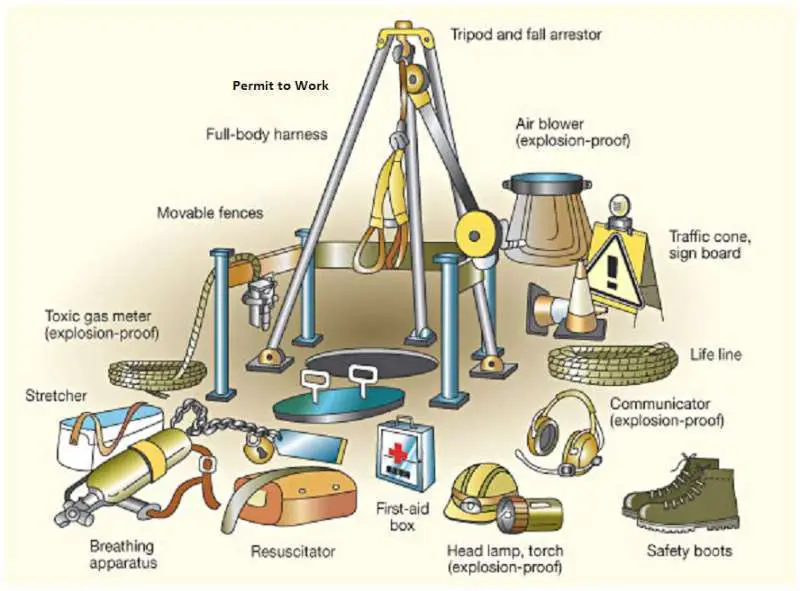
c. Employees will be trained in the proper use and care of the gas meter, full-body harness, and lifelines. You can also check How to check gas inside confined space with Ventis MX4
3.7 OFF-SITE RESCUE AND EMERGENCY SERVICES

a. The rescue service shall be informed of the associated hazards they may confront during a rescue. How to make confined space entry procedure
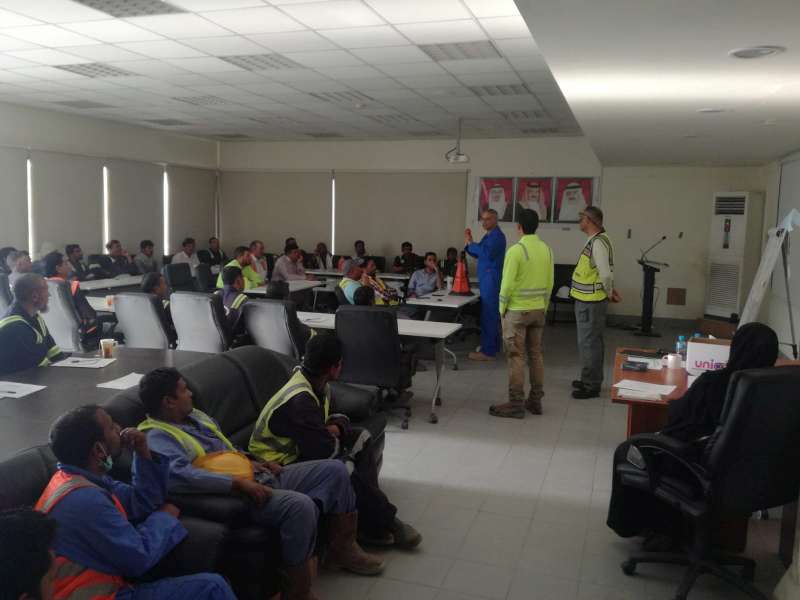

b. The rescue service shall be provided access to all permit-required confined spaces for which rescue may be necessary so that they can develop appropriate plans.
c. Unauthorized personnel shall not attempt a rescue operation.
3.8 RETRIEVAL SYSTEMS
a. Each authorized entrant shall use a full-body harness with a retrieval line attached at the center of the entrants back near the shoulder level.
b. Retrieval lines shall be attached to a fixed point outside the permit space in such a manner that rescue can begin as soon as the rescuer becomes aware of the need for rescue.
3.9 WELDING AND CUTTING OPERATIONS
a. Employees shall not be permitted to engage in hot work in a confined space until a complete evaluation has been made by the Project/ Safety Manager or Safety Officer. What is confined space and its characteristics
b. Before gas welding or burning is started in a confined space, check hoses for leaks.
c. Compressed gas bottles are strictly prohibited from being taken into a confined space.
d. Space must be tested for an explosive atmosphere before a torch is lighted inside the space.
e. No plant, tank or vessel which contains or has contained any explosive or flammable substances shall be subjected to any welding, brazing or soldering operations or to any cutting operation which involves the application of heat, until all practical steps have been taken either to remove the substance or fumes arising from them, or to render them non-flammable or non-explosive.
The Entry Supervisor shall approve the commencement of these operations. Continuous monitoring or periodic checks, as applicable, shall be carried out to ensure that the confined space is maintained in a safe condition. How to make confined space entry procedure
3.10 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
Particular care shall be taken when it is necessary to use an internal combustion engine in the vicinity of a confined space. Adequate arrangements shall be made to ensure that the products of combustion are extracted to a point remote from the work area, to prevent oxygen depletion or a build-up of carbon monoxide or other potentially hazardous gases within the confined space.
INTERNAL MOVING PARTS
Where the confined space is fitted with internal moving parts or mechanically operated doors, the drive shall be disconnected or the driving motor isolator shall be locked in the “off” position.
SOLVENTS, PAINTS, ETC
An adequate supply of fresh air shall be provided by natural ventilation or by means of a blower or from a compressed air line, particularly when cleaning with solvents, painting (with or without aerosols) or doing any work which may create toxic fumes. Additionally, it may be necessary to have a compressed air breathing set available, with another set on standby. How to make confined space entry procedure.
EXPLOSIVE OR FLAMMABLE SUBSTANCES
No explosive or flammable substance shall be placed in any plant, tank or vessel which has been subjected to heat, until it has cooled, thus preventing any risk of ignition.
3.14 MISCELLANEOUS EQUIPMENT
No electrical lamp, torch, monitoring or other equipment, which may constitute a means of ignition, shall be taken into any plant or vessel which has contained any explosive or flammable substance until it has been proved by a test carried out by the Entry Supervisor or Safety Officer that the concentration of flammable gasses or vapors has been reduced to a value well below the lower flammable limit.
3.15 VIOLATION OF THESE PROCEDURES
How to make confined space entry procedure. Entry into a confined space, which has the potential to be immediately dangerous to life and health, without the issuance of a permit and adherence to the previously outlined entry procedures, may result in the employee(s) immediate discharge.
4.0 RECORD KEEPING
Canceled confined space entry permits must be retained for a period of at least one (1) year. what is confined space safety and measures