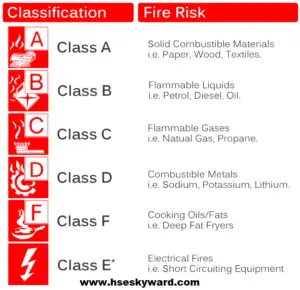
what are classes of fire
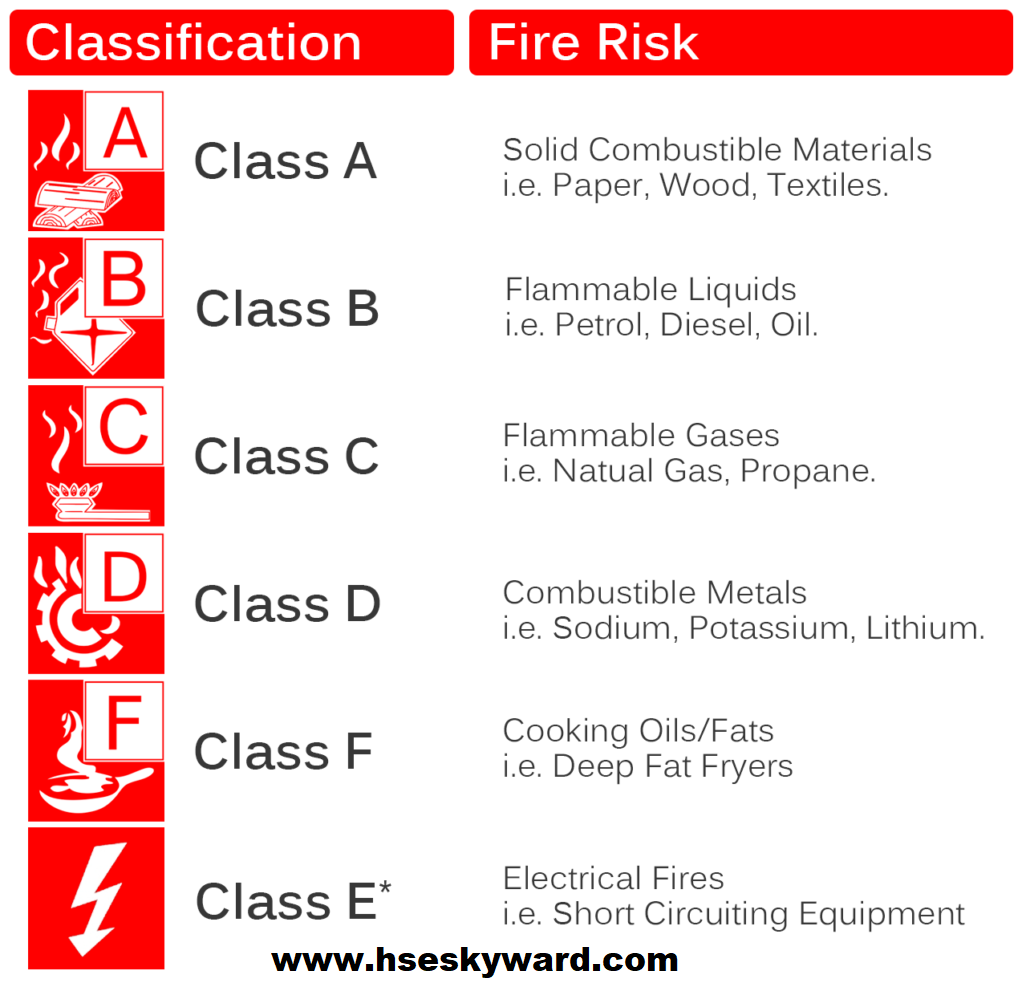
Did you know that there are 5 different fire classes?. Before you start extinguishing the fire, you must determine what exactly is burning. You can then start extinguishing the fire. International agreements have been made on a number of main classes of the fire. We call this the 5 different fire classes.
A fire extinguisher is indicated with a symbol for which fire the extinguishing agent is suitable. It is therefore not possible to extinguish all types of fires with every fire extinguisher. Below you will find all the fire classes.
Fire classes are used to classify all flammable substances and have a decisive influence on the choice of the right extinguishing agent in firefighting. Skilled experts know, due to the fire class, which extinguishing agent to use. In the following article, we would like to show you the differences in the individual fire classes since the choice of the wrong extinguishing medium in case of fire can have dangerous devastating effects. The use of a fire extinguisher that is not suitable for extinguishing the relevant fire class may result in increased fire expansion or, in the worst case, an explosion.
Each fire extinguisher has a pictogram showing the relevant fire rating. This pictogram shows you whether the fire extinguisher is suitable for extinguishing the respective fire source or not. Combustible materials are classified according to the European Standard EN 2 into five different fire classes, which are identified as fire classes A, B, C, D, and F.
What are classes of fire
Overview of all fire classes






What are international standards for classes of fire
Class A fire
This is a fire of solids such as wood, paper, furniture, and curtains.
Suitable extinguishing media:
fire hose reel, powder extinguisher, spray foam extinguishers, and a fire blanket.
The fire class A all solid substances that occur predominantly in nature fall. These substances usually burn with the formation of embers, so an extinguishing agent must be used, which not only fights the flames but also quenches the embers. For this purpose, water is very good for fire extinguishers that are filled with foam or powder.
However, powder extinguishers should only be used as ABC extinguishers because they contain a firing powder. Fire class A includes substances such as wood, coal, textiles, paper, some plastics, hay, straw, and fibers.
Class B fire
This is a fire of liquid substances such as gasoline, diesel oil, acetone, and wax.
Suitable extinguishing agent:
spray foam extinguishers, CO² extinguishers, or powder extinguishers.
The fire class B includes all liquid, flammable substances and substances that become liquid due to the effect of heat. The liquid substances include, for example, gasoline, oils, fats, paints, varnishes, and alcohol. The substances that melt and become fluid when heated include, for example, plastics such as PVC, wax, tar, resin and numerous plastics.
Class B substances burn exclusively with flames and do not produce embers. The substances mentioned must be taken to ensure that they are never extinguished in case of fire with water! The water would evaporate and due to the burning liquid, a deflagration would result.
Substances of fire class B are smothered by the extinguishing agent. For this purpose, a fire blanket can be used or foam fire extinguishers, ABC fire extinguishers, fire extinguishers with BC powder and CO2 extinguishers (carbon dioxide).
Class C fire
this fire includes all flammable gases such as propane, LPG, natural gas, methane, city gas, butane, ethyne (acetylene) and hydrogen.
The best way to extinguish a Class C fire is to be the first to shut off the gas tap, otherwise, there is a risk of explosion. They do not produce embers, but only burn with a flame. In the case of gas fires, it should be noted that they cannot be extinguished with water, foam or carbon dioxide (CO2) and thus are completely unusable as extinguishing agents. Extinguishing media are fire extinguishers with ABC powder and BC powder.
Suitable extinguishing agent:
powder extinguishers.
Class D fire
Class D is a fire made of metal such as aluminum, metal, magnesium
Suitable extinguishing agent:
Powder extinguishers suitable for fire class D, also known as metal fire extinguishers.
Class D fire is very rare in everyday life. Since they are fires of combustible metals such as Aluminium, magnesium, sodium, potassium or lithium. These metals burn only at very high temperatures of well over 1000 ° C and are considered very difficult to erase.
Metal fires are graded as class D. these fires should never be extinguished with water, as the water would split into water vapor and oxygen at high temperatures, which would result in the formation of oxyhydrogen gas with a high risk of explosion. Metal fires are extinguished exclusively with special metal firing powder, dry sand, dry cement powder or dry litter or cattle salt.
Class E fire
These are electrical fires. Please note: fire class E has been canceled because electricity can be a cause of the fire but not itself. For example, a computer will burn due to a short circuit. The computer is on fire and not electricity. This is then fire class A fire and not E, the reason for discussing here for the knowledge purpose for the beginners.
Class F fire
the fire class F includes fires of edible fats and cooking oils, which are typically found in kitchens in everyday life. Because of the great danger, the fire class F was included in the classification of the European standard EN 2 in 2005.
Quickly it happened and the frying pan with the hot cooking oil is forgotten for a moment on the stove. With overheated edible fat and cooking oil, there is a high risk of re-ignition, which often leads to serious injuries.
Fat burns should never be extinguished with water as water is lighter than burning fat. In a quenching test with water, the extinguishing water would quickly sink in the burning fat and evaporate. The resulting water vapor would suddenly shoot up and tear the hot fat with it, creating a jet flame.