Classes of fire according to international standards
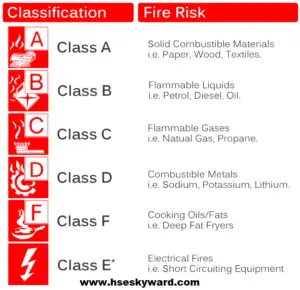
Classes of fire or Fire class is a term used to indicate the kind of fire, in connection to the burning materials which have (or could be) lighted/ignited. This has forward effects on the sort of concealment or stifling materials that can be used. Class letters are regularly allocated to the various kinds of fire, however, these vary between regions. There are discrete or different standards in Europe, the United States, and Australia.
There are two different standards of Fire types.
1. Classes of fire according to American standard (NFPA)
2. Classes of fire according to European standards
3.Classes of fire according to Australian standard
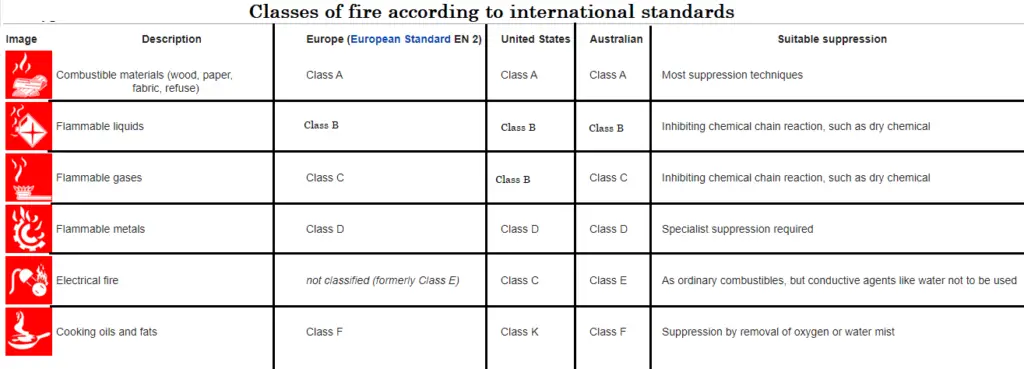
America standard (NFPA)
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) is a global not-for-profit association gave to disposing of death, damage, property and monetary misfortune happening because of fire, electrical and related hazards. In 2018, the NFPA professes to have 50,000 individuals and 9,000 volunteers working with the association through its 250 specialized committees. NFPA defines classes of the fire as below: there are five types of fire which are the following:-
1. Class A
(solid fire) in this fire combustible materials are Wood, fabric, paper, trash
2. Class B
(Liquid fire) in this fire combustible materials are oils and paints, kerosene, and gasoline
3. Class C
(Electrical fire) in this fire combustible materials is Energised electrical equipment.
4. Class D
(Metal fire) in this fire combustible materials are titanium, magnesium, aluminum, and potassium.
5. Class K
(Kitchen fire) in this fire combustible materials are Cooking oils
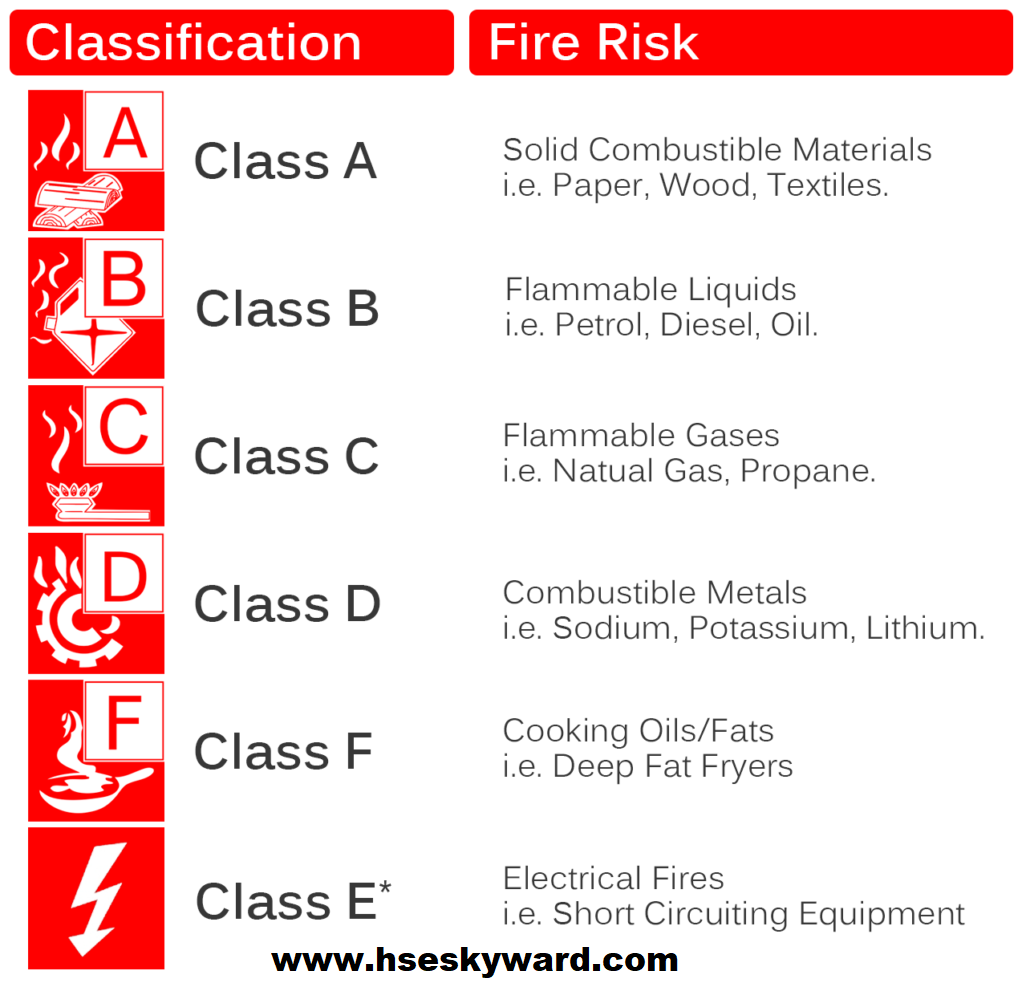
Classes of fire according to the Australian standard.
There are six types of fire which are the following:-
1. Class A
(solid fire) in this fire combustible materials are Wood, fabric, paper, trash
2. Class B
(Liquid fire) in this fire combustible materials are oils and paints, kerosene, and gasoline
3. Class C
(Gaseous fire) in this fire combustible materials are LPG, CNG, and propane.
4. Class D
(Metal fire) in this fire combustible materials are titanium, magnesium, aluminum, and potassium
5. Class E
(Electrical fire) in this fire combustible materials is Energised electrical equipment.
6. Class F
(Kitchen fire) in this fire combustible materials are Cooking oils.